Characteristic Beam Patterns of X-ray Include Which of the Following
In this excerpt the author describes how the scientists are searching for X-ray patterns that signal black holes. Common targets used in x-ray tubes include Cu and Mo which emit 8 keV and 14 keV x-rays with corresponding wavelengths of 154 Å and 08 Å respectively.
12 X Ray Diffraction And Mineral Analysis Mineralogy
The controlling factor for beam quality is kVp.
. An ionizing effect on air 3. Characteristics of X-ray Beam We include beam quality beam quantity and beam intensity in any discussion related to the X-ray beam. When a free electron fills the shell a x-ray photon with energy characteristic of the target material is emitted.
C The rotor increases its rotation for higher x-ray production. They are differentially absorbed by different forms of matter. Start studying Chapter 8 Dental X-Ray Characteristics.
Imaginary perpendicular ray at its center is called central ray. A penetrating effect on all matter 2. The defining characteristics of X-raystheir ability to penetrate optically opaque materials their wavelengths of atomic dimension the high energy of individual X-ray photonslead to a wide range of industrial medical and scientific applications.
Body parts further away from the detector are magnified compared with those that are closer. 3 Electrons that are emitted form a space charge- cloud around the filament. They penetrate various materials.
Therefore we could say that the description is based on the characteristics of X-ray patterns which can signalize a black hole. May be manufactured with a positive beam limiting device. X-ray divergence patterns can be described by photons directed linearly towards the center whereas those on the periphery tend to splay out more radially.
Specialized X-ray sources detectors and analysis techniques have been developed to address a range of questions from the study of. Projection The axial plane divides the body into what sections. When an outer shell electron moves to fill the space created in the inner shell energy in the form of an x-ray photon is emitted.
2Heating causes thermionic emission to occur- boiling off of electrons specifically outer shell electrons. The external structure of the x-ray tube includes the support structure the protective housing and the. A More electrons are produced at the cathode.
X-ray energy is measured in kiloelectron-volts keV 1000 electron volts. In this case the word signals a characteristic of an X-ray pattern. 1 Current will heat the tungsten filament.
The physician orders a chest X-ray as part of the preventive exam. The cross section of the xray beam at the point where it is utilized is called the radiation field. These x-ray spectra represent local L and partial P electron density of states DOS because of the.
Travelling at the speed of sound. These different techniques are generally termed photolithography X-ray lithography electron beam lithography or ion beam lithography depending on the radiation employed. Braggs law is used to determine a crystal parameters from its characteristic x-ray pattern.
Often the product of the tube current and exposure time is considered as one entity the mAs milliampere-second. Please contact SERC serccarletonedu for more information. Approximately 80 of the population of X-rays within the X-ray beam consists of X-rays generated in this way.
The negative side of the x-ray tube holds the. The x-ray beam is polyenergetic many energies and consists of a wide range of energies known as the x-ray emission spectrum. 1 while the x-ray absorption spectra reflect the unoccupied molecular orbitals MO.
These two focal projections are necessarily about 90 apart in the plane normal to the filament-anode axis. The most widely used support structure for the x-ray tube is the. Davis has his yearly preventive medicine exam.
The x-ray emission spectra reflect the occupied electronic structure as shown in Fig. When an electron passes near the nucleus it is slowed and its path is deflected. Cross section of xray beam is called the radiation field.
X-Ray beams that are parallel with wide projection of the filament have a focal shape of a line. The pattern-transferring processes include four key steps. The path of the X-ray beam is known as.
Currently the most common form of beam restriction 4. Consider the following types beam restrictors and match them to their respective characteristics 1. Occasionally magnification can be helpful in localising abnormalities.
The kV mA and exposure time are the three major selectable parameters on the x-ray generator control panel that determine the x-ray beam characteristics. Classified as the simplest form of a beam restrictor 2. X-ray emission spectra of solids and molecules are methods of measuring electronic structure of matter 15.
They are a form of electromagnetic radiation. From the focal spot the xray diverge into space forming the cone-shaped primary xray beam. 1 solution-based wet chemical etching procedures 2 dry etching in a reactive plasma 3 doping using ion implantation techniques.
The lowest energies are always approximately 15 to 20 keV and the highest energies are always equal to the kVp set on the control panel. They affect photographic emulsions. X-rays travel in straight lines.
Consists of moving horizontal and vertical lead strips 3. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Beam profiles and paths of the photons also influence the quality and characteristics of an image.
Provenance No information about the origin of this particular item is recorded. B Target interaction efficiency increases at the anode. However kVp is also a controlling factor for beam quantity because when kVp is increased.
Characteristics of x-ray photons include 1. Therefore it is essential to distinguish between these concepts and understand the factors that influence them. X-rays travel in straight lines and a beam of X-rays diverges from its source.
Energy lost is emitted as a bremsstrahlung X-ray photon. For example an 80-kVp x. Bremsstrahlung Braking radiation.
Characteristic x-rays are caused by the ejection of an electron from an inner shell of an atom hit by the incident x-ray. X-Ray beams that are parallel with the narrow projection of the filament have an approximate focal shape of a square which is usually labeled as a spot. As a result the anatomy located on the periphery of the beam profile and lateral to the.
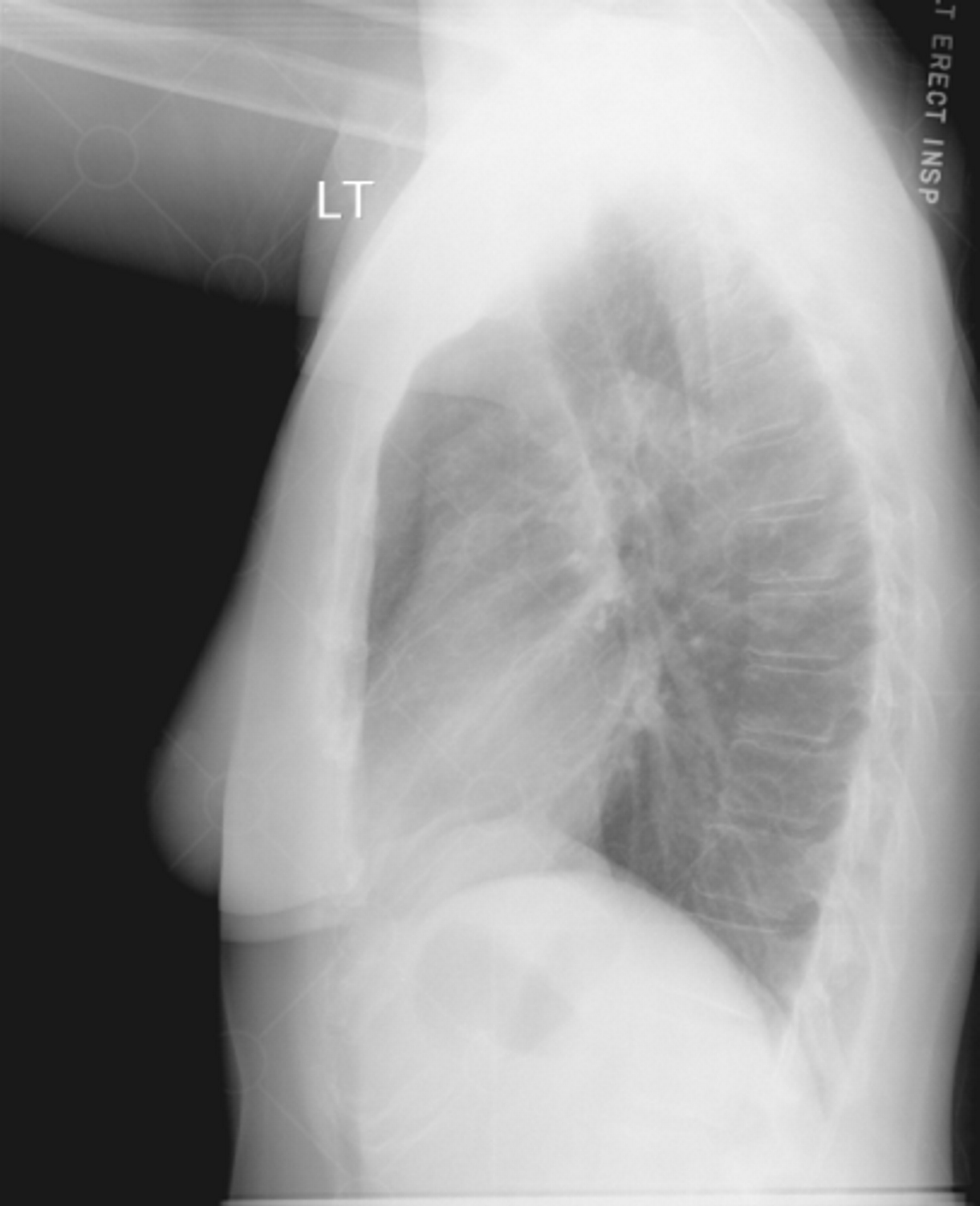
Digital Radiography Image Artifacts Radiology Suny Upstate Medical University
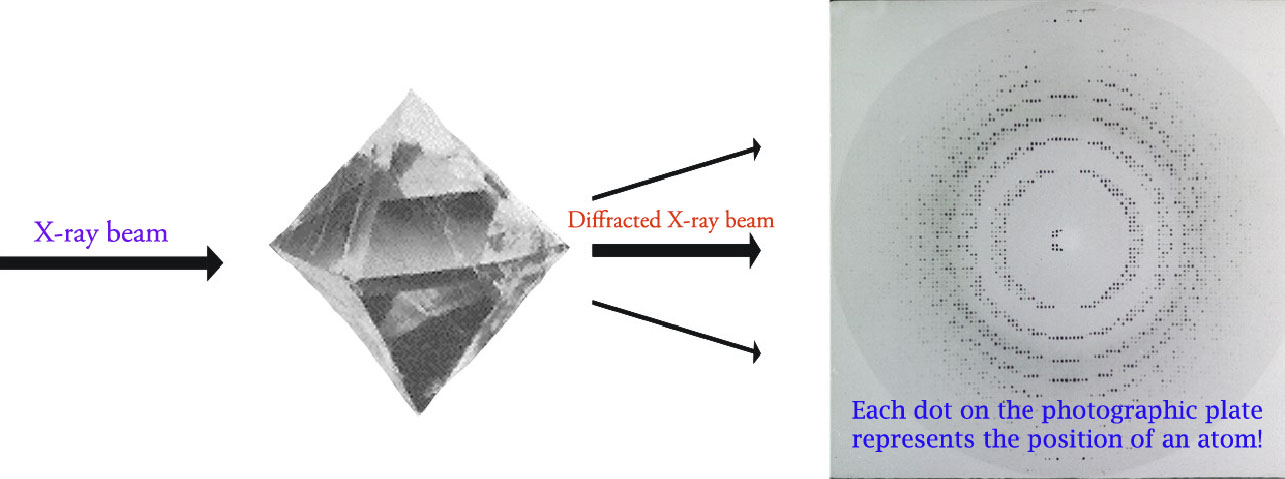
Diffraction Basics Chemical Instrumentation Facility Iowa State University
No comments for "Characteristic Beam Patterns of X-ray Include Which of the Following"
Post a Comment